In this post, we will see how to manage Dictionary with Python.
CREATE A DICTIONARY
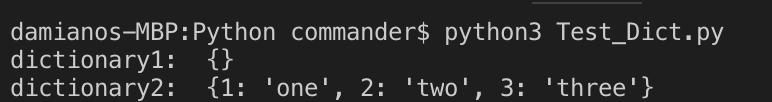
# empty dictionary
dict1 ={}
# dictionary
dict2 = {1:"one", 2:"two", 3:"three"}
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
print(f"dictionary2: {dict2}")
ADD ITEMS
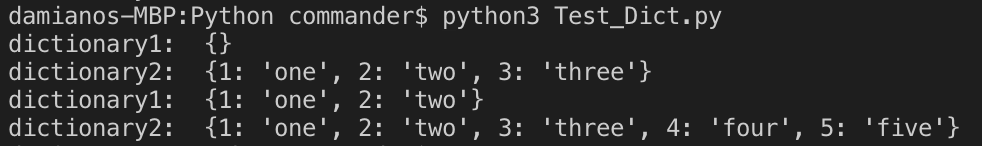
# empty dictionary
dict1 ={}
# dictionary
dict2 = {1:"one", 2:"two", 3:"three"}
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
print(f"dictionary2: {dict2}")
# add items
dict1[1]='one'
dict1[2]='two'
dict2[4]='four'
dict2[5]='five'
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
print(f"dictionary2: {dict2}")
UPDATE ITEMS
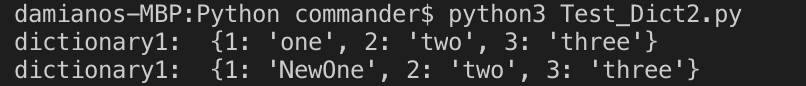
# dictionary
dict1 = {1:"one", 2:"two", 3:"three"}
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
#update value
dict1[1]='NewOne'
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
DELETE ITEMS
# dictionary
dict1 = {1:"one", 2:"two", 3:"three"}
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
#delete value using the key
del dict1[3]
print(f"dictionary1: {dict1}")
GET VALUES
# dictionary
dict1 = {1:"one", 2:"two", 3:"three"}
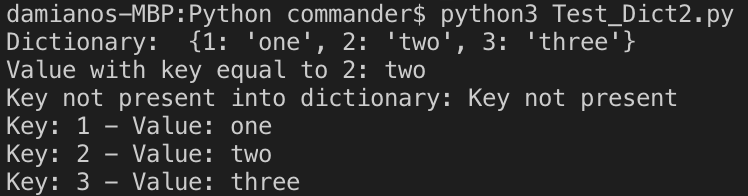
print("Dictionary: ", dict1)
# get value using the key
print(f"Value with key equal to 2: {dict1[2]}")
# With the method get, in case of key not present, the system
# will show a default value instead to generate an error
print(f"Key not present into dictionary: {dict1.get(5,'Key not present')}")
# print all items in a dictionary
for i in dict1:
print(f"Key: {i} - Value: {dict1[i]}")
COPY A DICTIONARY
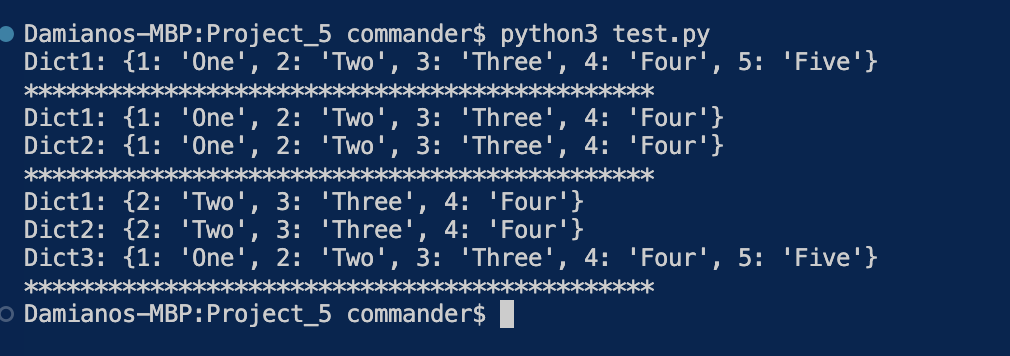
dict1 = {1: "One", 2: "Two", 3: "Three", 4: "Four", 5: "Five"}
dict2 = dict1
dict3 = dict1.copy()
print(f"Dict1: {dict1}")
print("*********************************************")
del dict1[5]
print(f"Dict1: {dict1}")
print(f"Dict2: {dict2}")
print("*********************************************")
del dict2[1]
print(f"Dict1: {dict1}")
print(f"Dict2: {dict2}")
print(f"Dict3: {dict3}")
print("*********************************************")
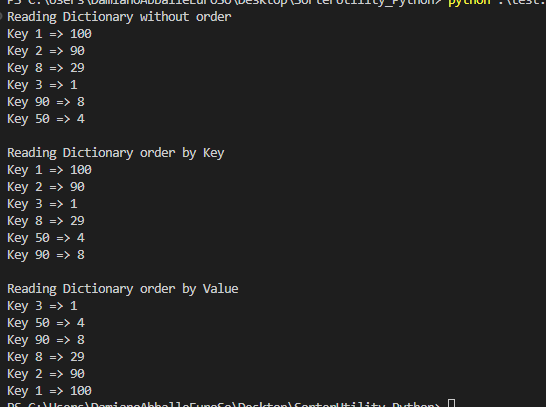
ORDER
# we create a Dictionary<int,int>
dict1 = {1:100, 2:90, 8: 29, 3: 1, 90: 8, 50: 4}
print("Reading Dictionary without order")
for item in dict1:
print(f"Key {item} => {dict1[item]}")
print()
# Order by Key
sort_forKey = dict(sorted(dict1.items(), key=lambda item: item[0]))
print("Reading Dictionary order by Key")
for item in sort_forKey:
print(f"Key {item} => {sort_forKey[item]}")
print()
# Order by Value
sort_forValue = dict(sorted(dict1.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
print("Reading Dictionary order by Value")
for item in sort_forValue:
print(f"Key {item} => {sort_forValue[item]}")